Abstract
Introduction
Post-transplantation cyclophosphamide (PTCy) and calcineurin inhibitor (CNI) based GVHD prophylaxis has shown lower rates of acute and chronic GVHD when compared with the traditional prophylaxis of calcineurin inhibitor (CNI) and methotrexate (MTX) in matched donor (related and unrelated) allo-HCT. The combination of PTCy with sirolimus as a calcineurin inhibitor-free GVHD prophylaxis has shown promising results with cumulative rates of grade II-IV acute and chronic GVHD in the range of 15-27% and 20-27% respectively in patients undergoing matched and haploidentical allo-HCT. We report a single center, nonrandomized comparison of patients undergoing matched donor allo-HCT receiving PTCy in combination with sirolimus (PTCy/Siro) with those receiving the standard GVHD prophylaxis of tacrolimus and MTX (Tac/MTX).
Methods
One hundred and sixteen consecutive patients who had undergone a MRD or MUD allo-HCT between January 2018 to January 2021 and received either PTCy with sirolimus or tacrolimus with methotrexate as GVHD prophylaxis regimens were eligible for inclusion. The selection of PTCy with sirolimus or tacrolimus with methotrexate as GVHD prophylaxis regimen was based on physician choice. Primary endpoints were cumulative incidence of acute (grade II to IV) and chronic GVHD. Secondary endpoints were a) neutrophil and platelet engraftment; b) overall survival (OS); c) non-relapse mortality (NRM); d) relapse; e) clinical infections and f) time to immunosuppression (IS) withdrawal. Kaplan-Meier method was used to estimate 1-year and 2-year freedom from long term adverse events, including chronic GVHD, relapse, NRM and OS. All tests were two-sided with alpha level set at 0.05 for statistical significance.
Results
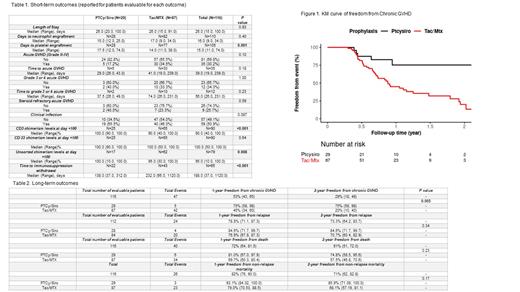
Out of a total of 116 patients undergoing MRD and MUD allo-HCT, 29 received PTCy/Siro and 87 Tac/MTX. Baseline characteristics were similar between the two arms except patients in PTCy/Siro were younger with median of 48 (range: 24-69) years vs. 61 (range: 20-73) years (p=0.004) in Tac/MTX. There was difference in primary indication for allo-HCT between the two arms with non-hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) being the most common in PTCy/Siro and acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in the Tac/MTX group. Patients receiving PTCy/Siro had a significantly higher median CD3 day 100 chimerism at 100 (90-100) vs. 90 (40-100) % (<0.001) and a significantly shorter median time to IS withdrawal at 138 (37-312) vs 232(66-1120) days for patients receiving Tac/MTX. There was no difference between the two arms for length of hospital stay and time to neutrophil engraftment, but PTCy/Siro had a significantly longer median time for platelet engraftment at 17.5 (12-74) vs.14 (11-38) days (p= 0.001). No significant difference was observed between the two arms for incidence of grade II to IV acute GVHD, grade III to IV acute GVHD, steroid refractory acute GVHD or clinical infections (Table 1). After a median follow up of 1.1 (range: 0-1.8) years, patients receiving PTCy/Siro were significantly less likely to have chronic GVHD with 2-year freedom from GVHD of 75% (95%CI: 58-98%) vs 20% (95%CI 10-40%), p=0.005 (Figure 1). There was no difference between the two arms for OS, disease relapse or non-relapse mortality (Table 2).
Conclusion
In this study, the combination of PTCy/Siro is associated with a significantly lower risk of chronic GVHD when compared against the traditional GVHD prophylaxis of CNI and methotrexate, despite significantly earlier IS withdrawal. Other long-term outcomes of interest remained comparable between the two arms. Chronic GVHD contributes to significant morbidity and mortality in patients undergoing allo-HCT. Newer strategies to limit the impact of chronic GVHD are needed. The results of our study warrant validation in a large, multicenter, randomized prospective trial.
Murthy: CRISPR Therapeutics: Research Funding. Foran: gamida: Honoraria; takeda: Research Funding; novartis: Honoraria; trillium: Research Funding; boehringer ingelheim: Research Funding; OncLive: Honoraria; abbvie: Research Funding; certara: Honoraria; sanofi aventis: Honoraria; syros: Honoraria; taiho: Honoraria; revolution medicine: Honoraria; bms: Honoraria; servier: Honoraria; pfizer: Honoraria; actinium: Research Funding; aptose: Research Funding; kura: Research Funding; h3bioscience: Research Funding; aprea: Research Funding; sellas: Research Funding; stemline: Research Funding.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal